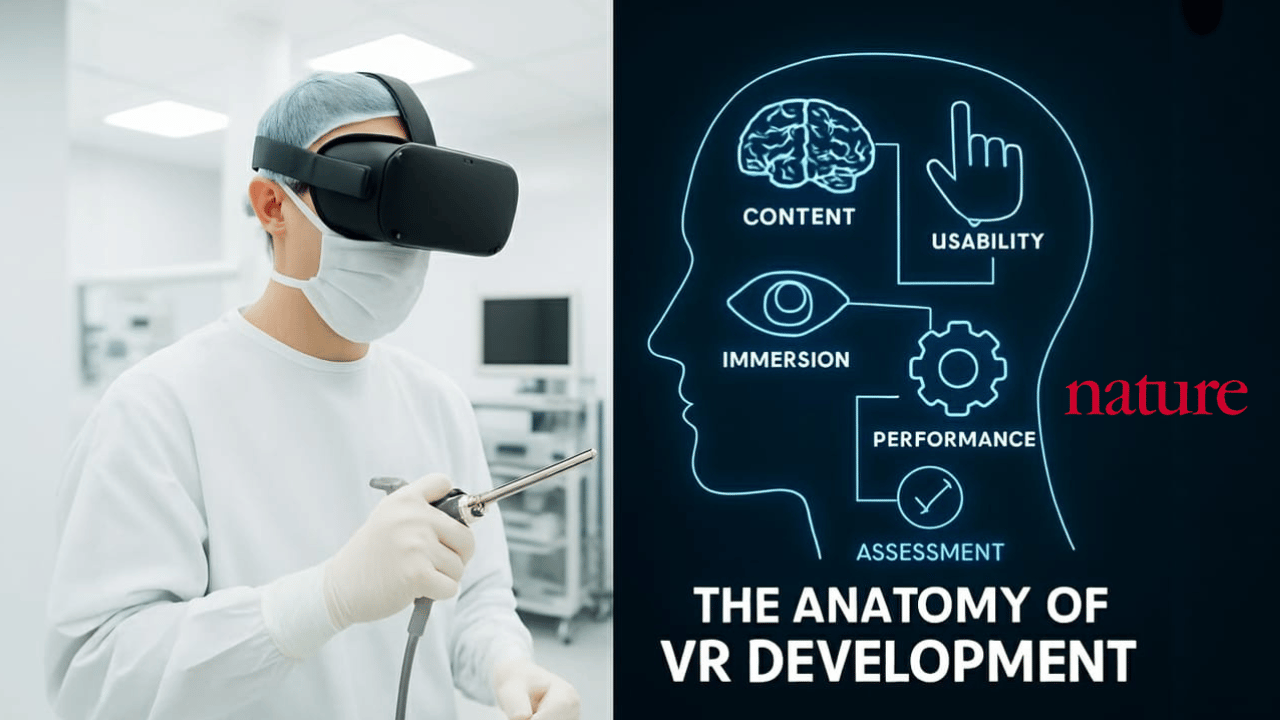
A new Nature study just outlined 80+ requirements for building effective VR anatomy apps.
Most readers won’t dig through dozens of pages of research—but that’s where we come in. We’ve pulled out the key findings. We’ll show you the requirements that matter most. And we’ll put them into context with our own work, like the VR endoscopy training project we built for Karl Storz.
Here’s the anatomy of VR development—in plain English.
VR Tool of the Week: Cognitive3D
When you build VR experiences, measuring them matters as much as building them.
Cognitive3D is a spatial analytics platform that lets you peer into exactly how users move, look, and interact in your 3D environments—going beyond simple metrics to deliver insight into why things happen.
It’s a key bridge between your development framework and data-driven optimization.
Key Features & Specs:
Captures over 3,000 data points per minute of XR activity (movement, gaze, object interactions)
Session replay: review user journeys in full 3D (move through recorded sessions from any angle).
Heatmaps & gaze mapping: see where users focus most in your environment.
Custom event tracking: define bespoke metrics for your training goals (e.g., tool usage, error events).
Performance & device analytics: monitor frame rate, latency issues, battery usage across hardware.
Cross-platform & SDK support: integrates with Unity, supports headsets & AR/VR devices
learn more here
The Study in a Nutshell
In February 2025, Nature Scientific Reports published a study that could change how we think about VR training.
The researchers reviewed dozens of anatomy apps and distilled what makes them effective. The result: a framework of 23 content needs and 57 technical requirements—more than 80 checkpoints that define whether a VR app actually works as a training tool. This matters because VR is no longer a novelty. Companies are investing serious money in immersive training, but until now, there hasn’t been a clear playbook. Most projects were built on intuition, trial-and-error, or the priorities of whoever held the budget. With this framework, we now have evidence-based guidance: what to include, what to avoid, and how to measure success.
And it echoes what we’ve already seen firsthand in our own projects, like Karl Storz’s VR endoscopy training.
HUGE XR NEWS (September 2025 Edition)
Meta is rolling out an updated engine for Horizon Worlds, claiming faster loading times and support for “well over 100” users in a single space. (learn more)
Samsung’s long-rumored Android XR headset is expected to launch on October 21, running on Android XR and powered by a Snapdragon XR2+ Gen 2 chipset. (learn more)
Samsung reportedly delayed the launch of Project Moohan to better coordinate marketing and quality control, despite earlier rumors of a September release. (learn more)
According to a new market analysis, the XR/spatial computing market could exceed $100 billion in 2025, with longer-term forecasts in the $200–300 billion range. (learn more)
Researchers published a study on digital twin XR tourism applications, showing VR tours deliver strong user presence but also highlight usability and motion sickness challenges. (learn more)
Content Requirements (What to Teach)
The first pillar of the Nature framework is content. Out of the 80+ requirements, 23 focus on what’s being taught—accuracy, relevance, and alignment with the learner’s goals.
Here’s the distilled list of the 23 content requirements the researchers identified:
Accuracy | Completeness | Curriculum alignment |
Sequencing | Clear objectives | Clinical relevance |
Expert validation | Depth of explanation | Standard terminology |
Contextualization | Anatomy integration | Step-by-step guidance |
Progressive difficulty | Real-world scenarios | Case-based examples |
Error prevention cues | Feedback loops | Assessment capability |
Knowledge checks | Repetition opportunities | Learner adaptability |
Cultural/ethical alignment | Updates & revisions | — |
When we worked with Karl Storz, this principle was front and center.
Endoscopy is a delicate procedure, and any mistake in content could have real consequences in the operating room.
So the VR training app was built directly on surgical guidelines, vetted by practicing doctors, and reviewed at every development stage.
Technical Requirements (How to Teach It)
If content is the “what,” the technical side is the “how.”
The Nature study lists 57 technical requirements that shape whether VR training is usable, immersive, and effective. To make this easier to grasp, we can group them into five big buckets:
Usability | Interactivity | Immersion |
Simple navigation | Realistic object handling | High-quality graphics |
Clear interface | Responsive controls | Spatial sound |
Low cognitive load | Immediate feedback | Accurate 3D models |
Accessibility | Error correction | Realistic physics |
Consistent flow | Hands-on practice | Presence-inducing environment. |
Performance | Assessment & Support |
Stable 60+ fps | Progress tracking |
Low latency | Performance analytics |
Optimized file size | Adaptive difficulty |
Cross-platform | Instructor support |
Hardware reliability | Exportable results |
Why This Matters for Industry
The Nature study may have focused on anatomy apps, but the implications reach far beyond medical training.
Whether you’re teaching a surgeon, a factory technician, or a pilot, the same anatomy of VR development applies. Healthcare companies need accuracy and trust. Manufacturing firms need usability and performance for large teams. Aviation requires immersion and assessment to ensure safety.
In every case, the framework points to the same truth: VR works only when content and technical requirements align.
This is why projects fail when they chase flashy features without a structured backbone. A beautiful simulation with poor usability won’t train anyone. A high-end headset with inaccurate content is a waste of budget. But when the anatomy is respected, VR becomes more than a gadget—it becomes a scalable tool that improves learning outcomes, reduces error rates, and accelerates workforce readiness. That’s what made the Karl Storz project successful.
And it’s why this framework is so valuable for any company considering VR today.
Mastermind’s Takeaway
The big picture is clear: With frameworks like Nature’s and real-world proof from projects like Karl Storz, the anatomy of VR development is now mapped out.
Content. Technical design. Validation. These are the pillars that make the difference between a flashy demo and a trusted training tool
So the question is—how does this look inside your organization?
Or, if you’re a consultant, how do you present this anatomy to a potential client in a way that wins their trust?
That’s exactly where we come in.
Book a call with us, and we’ll show you how to apply this framework directly to your industry or consulting practice—step by step, with concrete examples from our past builds.
That’s a wrap
Talk soon!
Bruno Filkin
Founder, Mastermind VR
VR Strategy Consultation
Ready to explore VR training for your team?
Take the Next Step
Let us review your project and discuss possible development and production details.
👇🏼